In this Article
- INSTR Function
- Instr Example
- Instr Syntax
- Instr Start Position
- Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
- InstrRev Function
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- InString Examples
- If String Contains Substring
- Find Text String in a Cell
- Find Position of a Character in a String
- Search String for Word
- If Variable Contains String
- Instr and the Left Function
- Using Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
INSTR Function
The VBA Instr Function checks if a string of text is found in another string of text. It returns 0 if the text is not found. Otherwise it returns the character position where the text is found.
The Instr Function performs exact matches. The VBA Like Operator can be used instead to perform inexact matches / pattern matching by using Wildcards.
Instr Example
The following code snippet searches the string “Look in this string” for the word “Look”. The Instr Function returns 1 because the text is found in the first position.
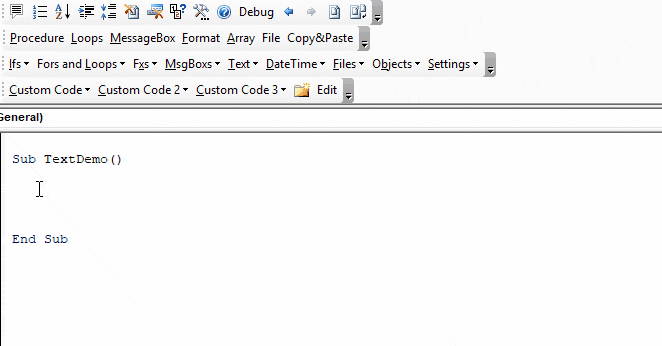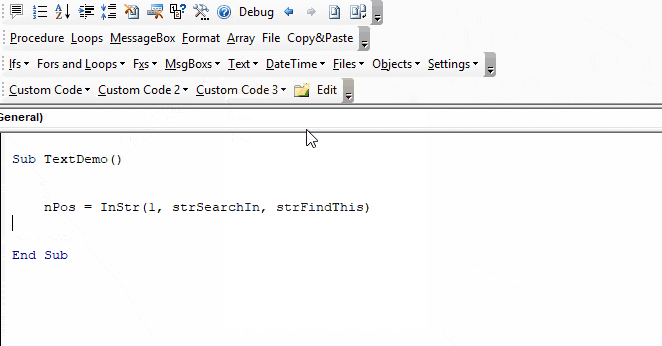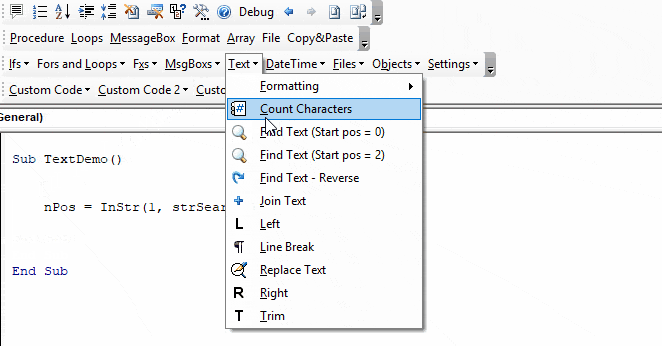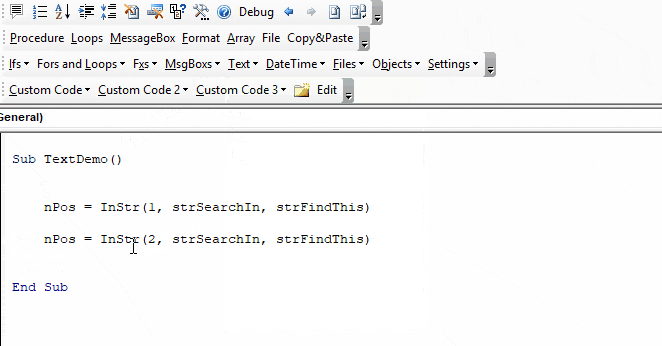
Sub FindSomeText()
MsgBox InStr("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubThis second example returns 7 because the text is found starting in the 7th position:
Sub FindSomeText2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "Look")
End SubImportant! The Instr Function is case-sensitive by default. This means “look” will not match with “Look”. To make the test case-insensitive read below.
Instr Syntax
The syntax for the Instr function is as follows:
Instr( [start], string, substring, [compare] )[start] (optional) – This optional argument is the starting position of the search. Enter 1 to start searching from position 1 (or leave blank). Enter 5 to start searching from position 5. Important! The INSTR function calculates the character position by counting from 1 NOT from the [start] position.
string – The string of text to search in.
substring – The string of text to find in the primary string.
[compare] (optional) – By default, Instr is case-sensitive. By setting this argument you can make Instr Case insensitive:
|
Argument vb Value |
Argument Integer | Description |
| vbBinaryCompare |
0 |
(Default) Case-sensitive |
|
vbTextCompare |
1 |
Not Case-sensitive |
|
vbDatabaseCompare |
2 |
MS Access Only. Uses information in the database to perform comparison. |
Instr Start Position
The Instr start position allows you to indicate the character position where you will begin your search. Keep in mind however, the Instr output will always count from 1.
Here we set the start position to 3 to skip the first B:
Sub Instr_StartPosition()
MsgBox InStr(3, "ABC ABC", "B")
End SubThe result is 6 because the second B is the 6th character in the string.
Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
By default, VBA treats “L” different from “l”. In other words, VBA is case-sensitive. This is true of all text functions. To make VBA case-insensitive, set the [compare] argument to 1 or vbTextCompare.
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase()
MsgBox InStr(1, "Don't Look in this string", "look", vbTextCompare)
End SubAlternatively, you can add Option Compare Text to the top of your code module:
Option Compare TextOption Compare Text
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "look")
End SubOption Compare Text will impact all of the code in that module. I personally place this at the top of any module that deals with text because I never care about case differences.
InstrRev Function
The Instr Function searches from the left. Instead you can search from the right using the InstrRev Function. The InstrRev Function works very similarly to the Instr function.
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubJust like the Instr function this will return 1 because there is only one instance of “Look” in the text. But if we add a second “Look”, you’ll see that it returns the position of the right-most “Look”:
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string Look", "Look")
End SubNext we will review more Instr examples.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
InString Examples
If String Contains Substring
Here we will use an If statement to test if a string contains a a substring of text:
Public Sub FindSomeText()
If InStr("Look in this string", "look") = 0 Then
MsgBox "No match"
Else
MsgBox "At least one match"
End If
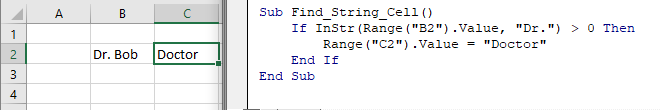
End SubFind Text String in a Cell
You can also find a string in a cell:
Sub Find_String_Cell()
If InStr(Range("B2").Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
Range("C2").Value = "Doctor"
End If
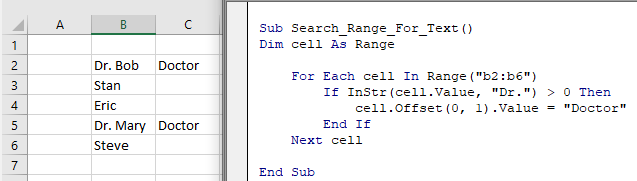
End SubOr loop through a range of cells to test if the cells contain some text:
Sub Search_Range_For_Text()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b6")
If InStr(cell.Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Doctor"
End If
Next cell
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Find Position of a Character in a String
This code will find the position of a single character in a string and assign the position to a variable:
Sub Find_Char()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "L")
End SubSearch String for Word
This code will search a string for a word:
Sub Search_String_For_Word()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "Look")
If n = 0 Then
MsgBox "Word not found"
Else
MsgBox "Word found in position: " & n
End If
End SubIf Variable Contains String
This code will test if a string variable contains a string of text:
Sub Variable_Contains_String()
Dim str As String
str = "Look Here"
If InStr(str, "Here") > 0 Then
MsgBox "Here found!"
End If
End SubInstr and the Left Function
Instr can be used along with other text functions like Left, Right, Len, and Mid to trim text.
With the Left function you can output the text prior to a string of text:
Sub Instr_Left()
Dim str As String
Dim n As Long
str = "Look Here"
n = InStr(str, "Here")
MsgBox Left(str, n - 1)
End SubUsing Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
To learn more, read our article: VBA text functions
<<Return to VBA Examples
| title | ms.prod | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Finding and Replacing Text or Formatting |
word |
9ab9f4a7-9833-5a78-56b0-56a161480f18 |
06/08/2019 |
medium |
Finding and replacing is exposed by the Find and Replacement objects. The Find object is available from the Selection object and the Range object. The find action differs slightly depending upon whether you access the Find object from the Selection object or the Range object.
Finding text and selecting it
If the Find object is accessed from the Selection object, the selection is changed when the find criteria is found. The following example selects the next occurrence of the word «Hello.» If the end of the document is reached before the word «Hello» is found, the search is stopped.
With Selection.Find .Forward = True .Wrap = wdFindStop .Text = "Hello" .Execute End With
The Find object includes properties that relate to the options in the Find and Replace dialog box. You can set the individual properties of the Find object or use arguments with the Execute method, as shown in the following example.
Selection.Find.Execute FindText:="Hello", _ Forward:=True, Wrap:=wdFindStop
Finding text without changing the selection
If the Find object is accessed from a Range object, the selection is not changed but the Range is redefined when the find criteria is found. The following example locates the first occurrence of the word «blue» in the active document. If the find operation is successful, the range is redefined and bold formatting is applied to the word «blue.»
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find .Text = "blue" .Forward = True .Execute If .Found = True Then .Parent.Bold = True End With
The following example performs the same result as the previous example, using arguments of the Execute method.
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Content myRange.Find.Execute FindText:="blue", Forward:=True If myRange.Find.Found = True Then myRange.Bold = True
Using the Replacement object
The Replacement object represents the replace criteria for a find and replace operation. The properties and methods of the Replacement object correspond to the options in the Find and Replace dialog box (Edit menu).
The Replacement object is available from the Find object. The following example replaces all occurrences of the word «hi» with «hello». The selection changes when the find criteria is found because the Find object is accessed from the Selection object.
With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .Text = "hi" .Replacement.ClearFormatting .Replacement.Text = "hello" .Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll, Forward:=True, _ Wrap:=wdFindContinue End With
The following example removes bold formatting in the active document. The Bold property is True for the Find object and False for the Replacement object. To find and replace formatting, set the find and replace text to empty strings («») and set the Format argument of the Execute method to True. The selection remains unchanged because the Find object is accessed from a Range object (the Content property returns a Range object).
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find .ClearFormatting .Font.Bold = True With .Replacement .ClearFormatting .Font.Bold = False End With .Execute FindText:="", ReplaceWith:="", _ Format:=True, Replace:=wdReplaceAll End With
[!includeSupport and feedback]
- Remove From My Forums
-
General discussion
-
Hi,
I am new to VBA. My requirement is that VBA code should find the path in the word document., some of the paths are present in the word document.
search criteria should start with \\ and end with .doc. Could anyone please help me out on how to provide the search criteria and is there any predefined methods present.
Thanks in advance.
Thanks,.
All replies
-
You’re doing a wildcard search for \\*.doc. In VBA, this is done as follows:
Sub FindIt() Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .Text = "\\*.doc" .Forward = True .Wrap = wdFindStop .Format = False .MatchCase = False .MatchWholeWord = False .MatchAllWordForms = False .MatchSoundsLike = False .MatchWildcards = True .Execute End With End Subor if you want to find all occurrences:
Sub FindIt() Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .Text = "\\*.doc" .Forward = True .Wrap = wdFindStop .Format = False .MatchCase = False .MatchWholeWord = False .MatchAllWordForms = False .MatchSoundsLike = False .MatchWildcards = True Do While .Execute ' Do something here Loop End With End Sub
Regards, Hans Vogelaar (http://www.eileenslounge.com)
-
Hi,
Thanks for the reply.
I getting the error when i use the code. please find below the changes i made
doc.ActiveDocument.Application.Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Text = «\\*.doc»
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindStop
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchWildcards = True
.Execute
End WithError :
Wrong number of arguments or invalid property
Thanks in advance.
-
Hi,
my requirement is from excel VBA i will open the document and will search in that document so only i have used
doc.ActiveDocument.Application.Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
Thanks
-
It might have helped had you said you were woking from Excel — it isn’t clear from the forum
In this case you could use the following which will list the paths in column A of the activesheet. You can change that in the code where marked in bold
Sub FindIt()
Dim wdApp As Object
Dim wdDoc As Object
Dim oRng As Object
Dim bStarted As Boolean
Dim i As Integer
On Error Resume Next
Set wdApp = GetObject(, «Word.Application»)
If Err Then
Set wdApp = CreateObject(«Word.Application»)
bStarted = True
End If
On Error GoTo 0
ActiveWorkbook.Save
‘Note that opening the document in Word if it is already open does not cause an error. It just sets the value to that open document.
Set wdDoc = wdApp.Documents.Open(«C:PathDocumentName.docx«)
Set oRng = wdDoc.Range
With oRng.Find
i = 1
Do While .Execute(FindText:=.Text = «\\*.doc», MatchWildCards:=True)
Range(«A» & i) = oRng.Text
oRng.collapse 0
i = i + 1
Loop
End With
wdDoc.Close 0
If bStarted Then wdApp.Quit
Set oRng = Nothing
Set wdDoc = Nothing
Set wdApp = Nothing
End Sub
Graham Mayor — Word MVP
www.gmayor.com
-
Edited by
Tuesday, December 30, 2014 7:25 AM
-
Edited by
-
Hi,
many Thanks for the reply
oRng.Text is always returning 0.
but i need the path to be written in the excel.
Thanks.
-
Hi,
My requirement is
I have 100 + word documents.
In that i have some paths hard coded in header,footer and in the content.
I need to take all those paths and need to write in excel sheet.
I know only the starting and the end letters of the document. starting is \\ and the end is .doc.
I need the complete paht between these.
Many thanks in advance.
Thanks
-
Apologies, the line
Do While .Execute(FindText:=.Text = «\\*.doc», MatchWildCards:=True)
should read
Do While .Execute(FindText:=»\\*.doc», MatchWildCards:=True)
It will however only work for the document body. If the string is in a different story range you will have to loop through those story ranges e.g.
Sub FindIt()
Dim wdApp As Object
Dim wdDoc As Object
Dim oRng As Object
Dim bStarted As Boolean
Dim i As Integer
On Error Resume Next
Set wdApp = GetObject(, «Word.Application»)
If Err Then
Set wdApp = CreateObject(«Word.Application»)
bStarted = True
End If
On Error GoTo 0
ActiveWorkbook.Save
Set wdDoc = wdApp.Documents.Open(«C:PathDocumentName.docx»)
i = 1
For Each oRng In wdDoc.StoryRanges
With oRng.Find
.MatchWildcards = True
Do While .Execute(FindText:=»\\*.doc»)
Range(«A» & i) = oRng.Text
oRng.Collapse 0
i = i + 1
Loop
End With
If oRng.StoryType <> wdMainTextStory Then
While Not (oRng.NextStoryRange Is Nothing)
Set oRng = oRng.NextStoryRange
With oRng.Find
.MatchWildcards = True
Do While .Execute(FindText:=»\\*.doc»)
Range(«A» & i) = oRng.Text
oRng.Collapse 0
i = i + 1
Loop
End With
Wend
End If
Next oRng
wdDoc.Close 0
If bStarted Then wdApp.Quit
Set oRng = Nothing
Set wdDoc = Nothing
Set wdApp = Nothing
End Sub
Graham Mayor — Word MVP
www.gmayor.com
-
Edited by
Graham MayorMVP
Tuesday, December 30, 2014 10:51 AM
-
Edited by
-
Hi,
Many Thanks for the reply. This helped me a lot. I have an another issue. When i try to convert my .dot files to .dotm the macros are not getting converted. Any Idea please.
Thanks
-
Hi,
Thanks for the help.
I there any way to find/search for the text in notepad through VBA.
Thanks
-
You can open a text file in Word, edit it and then save it.
Regards, Hans Vogelaar (http://www.eileenslounge.com)
-
Hi,
I have a footer document which is kept seperately in the some other folder.
I have thousands of files which refer to that footer document. I am planning to write an ini file to automate the usage.
IS there any way to read the data from the another file to one file using Ini.
Thanks.
|
Tanya15 Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Здравствуйте, подскажите, пожалуйста, как правильно прописать код VBA. |
|
V Пользователь Сообщений: 5043 |
и что дальше с этим делать будете? |
|
Пытливый Пользователь Сообщений: 4665 |
Варианты: Воспользоваться методом Find для диапазона. Вопрос — что дальше с ними делать надо? upd V, опередил с вопросом! Кому решение нужно — тот пример и рисует. |
|
Nordheim Пользователь Сообщений: 3154 |
#4 02.02.2018 11:12:01
Изменено: Nordheim — 02.02.2018 11:13:37 «Все гениальное просто, а все простое гениально!!!» |
||
|
Tanya15 Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Мой пример Sub Кнопка2_Щелчок() If Cells(i, j) = «яблоко» Then End Sub
В итоге считает только «яблоко», а зеленые и красные не учитывает. Необходимо, чтобы считал по всем ячейкам в которых содержится слово «яблоко» Изменено: Tanya15 — 02.02.2018 12:10:19 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Казанский Пользователь Сообщений: 8839 |
#6 02.02.2018 12:13:03 Tanya15,
|
||
|
Tanya15 Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Все так просто |
|
Nordheim Пользователь Сообщений: 3154 |
#8 02.02.2018 12:17:43 под ваш пример.
Изменено: Nordheim — 02.02.2018 12:20:58 «Все гениальное просто, а все простое гениально!!!» |
||
Функция VBA Instr проверяет, найдена ли строка текста в другой строке текста. Возвращает 0, если текст не найден. В противном случае он возвращает позицию символа, в которой находится текст.
Функция Instr выполняет точный Матчи. Вместо этого можно использовать оператор Like VBA для выполнения неточных совпадений / сопоставления с шаблоном с помощью подстановочных знаков.
Пример Instr
Следующий фрагмент кода ищет в строке «Искать в этой строке» слово «Искать». Функция Instr возвращает 1, потому что текст находится в первой позиции.
| 123 | Sub FindSomeText ()MsgBox InStr («Посмотри в этой строке», «Посмотри»)Конец подписки |
Этот второй пример возвращает 7, потому что текст находится начиная с 7-й позиции:
| 123 | Sub FindSomeText2 ()MsgBox InStr («Не смотри в эту строку», «Смотри»)Конец подписки |
Важный! Функция Instr деликатный случай по умолчанию. Это означает, что «взгляд» не будет совпадать с «взглядом». Чтобы сделать тест нечувствительным к регистру, читайте ниже.
Синтаксис Instr
Синтаксис функции Instr следующий:
| 1 | Instr ([начало], строка, подстрока, [сравнить]) |
[начало] (необязательно) — Этот необязательный аргумент — начальная позиция поиска. Введите 1, чтобы начать поиск с позиции 1 (или оставьте поле пустым). Введите 5, чтобы начать поиск с позиции 5. Важный! Функция INSTR вычисляет позицию символа, считая от 1 НЕ с позиции [начало].
нить — Строка текста для поиска.
подстрока — Строка текста, которую нужно найти в основной строке.
[сравнить] (необязательно) — По умолчанию Instr чувствителен к регистру. Установив этот аргумент, вы можете сделать Instr нечувствительным к регистру:
|
Аргумент vb Значение |
Целое число аргумента | Описание |
| vbBinaryCompare |
0 |
(По умолчанию) с учетом регистра |
|
vbTextCompare |
1 |
Нечувствительный к регистру |
|
vbDatabaseCompare |
2 |
Только MS Access. Использует информацию из базы данных для сравнения. |
Начальная позиция Instr
Начальная позиция Instr позволяет вам указать позицию символа, с которой вы начнете поиск. Однако имейте в виду, что вывод Instr всегда будет отсчитывать от 1.
Здесь мы устанавливаем начальную позицию на 3, чтобы пропустить первую букву B:
| 123 | Sub Instr_StartPosition ()MsgBox InStr (3, «ABC ABC», «B»)Конец подписки |
Результат — 6, потому что второй B — шестой символ в строке.
Тест INSTR без учета регистра
По умолчанию VBA рассматривает «L» иначе, чем «l». Другими словами, VBA чувствителен к регистру. Это верно для всех текстовых функций. Чтобы сделать регистр VBA нечувствительным, установите для аргумента [compare] значение 1 или vbTextCompare.
| 123 | Общедоступная подпрограмма FindText_IgnoreCase ()MsgBox InStr (1, «Не смотри в эту строку», «смотри», vbTextCompare)Конец подписки |
В качестве альтернативы вы можете добавить Option Compare Text в верхнюю часть модуля кода:
| 12345 | Вариант Сравнить текстОбщедоступная подпрограмма FindText_IgnoreCase2 ()MsgBox InStr («Не смотри в эту строку», «смотри»)Конец подписки |
Option Compare Text повлияет на весь код в этом модуле. Я лично помещаю это в начало любого модуля, имеющего дело с текстом, потому что меня не волнуют различия в регистрах.
Функция InstrRev
Функция Instr выполняет поиск слева. Вместо этого вы можете искать справа, используя функцию InstrRev. Функция InstrRev работает аналогично функции Instr.
| 123 | Sub FindSomeText_FromRight ()MsgBox InStrRev («Посмотри в этой строке», «Посмотри»)Конец подписки |
Как и функция Instr, она вернет 1, потому что в тексте есть только один экземпляр «Look». Но если мы добавим второй «Взгляд», вы увидите, что он возвращает положение самого правого «взгляда»:
| 123 | Sub FindSomeText_FromRight ()MsgBox InStrRev («Посмотрите в этой строке, Посмотрите», «Посмотрите»)Конец подписки |
Далее мы рассмотрим другие примеры Instr.
Примеры InString
Если строка содержит подстроку
Здесь мы будем использовать оператор If, чтобы проверить, содержит ли строка подстроку текста:
| 123456789 | Общедоступная подпрограмма FindSomeText ()Если InStr («Посмотри в этой строке», «посмотри») = 0, тоMsgBox «Нет совпадений»ЕщеMsgBox «Как минимум одно совпадение»Конец, еслиКонец подписки |
Найти текстовую строку в ячейке
Вы также можете найти строку в ячейке:
| 12345 | Sub Find_String_Cell ()Если InStr (Range («B2»). Value, «Dr.»)> 0, тоДиапазон («C2»). Значение = «Доктор»Конец, еслиКонец подписки |
Или прокрутите диапазон ячеек, чтобы проверить, содержат ли ячейки какой-либо текст:
| 12345678910 | Sub Search_Range_For_Text ()Тусклая ячейка как диапазонДля каждой ячейки в диапазоне («b2: b6»)Если InStr (cell.Value, «Dr.»)> 0 Тогдаcell.Offset (0, 1) .Value = «Доктор»Конец, еслиСледующая ячейкаКонец подписки |
Найти позицию символа в строке
Этот код найдет позицию одного символа в строке и присвоит эту позицию переменной:
| 1234 | Sub Find_Char ()Dim n As Longn = InStr («Вот, посмотри сюда», «L»)Конец подписки |
Строка поиска для слова
Этот код будет искать в строке слово:
| 12345678910 | Sub Search_String_For_Word ()Dim n As Longn = InStr («Вот, посмотри сюда», «Посмотри»)Если n = 0, тоMsgBox «Слово не найдено»ЕщеMsgBox «Слово найдено в позиции:» & nКонец, еслиКонец подписки |
Если переменная содержит строку
Этот код проверяет, содержит ли строковая переменная строку текста:
| 12345678 | Подпеременная_Contains_String ()Dim str As Stringstr = «Смотри сюда»Если InStr (str, «Here»)> 0, тоMsgBox «Вот нашел!»Конец, еслиКонец подписки |
Instr и левая функция
Instr можно использовать вместе с другими текстовыми функциями, такими как Left, Right, Len и Mid для обрезки текста.
С помощью функции Left вы можете вывести текст перед строкой текста:
| 1234567891011 | Sub Instr_Left ()Dim str As StringDim n As Longstr = «Смотри сюда»n = InStr (str, «Здесь»)MsgBox Left (str, n — 1)Конец подписки |
Использование Instr в Microsoft Access VBA
Все приведенные выше примеры работают в Access VBA точно так же, как и в Excel VBA.
Чтобы узнать больше, прочитайте нашу статью: Текстовые функции VBA