The reason why you always got True has already been given, so I’ll just offer another suggestion:
If your file is not too large, you can read it into a string, and just use that (easier and often faster than reading and checking line per line):
with open('example.txt') as f:
if 'blabla' in f.read():
print("true")
Another trick: you can alleviate the possible memory problems by using mmap.mmap() to create a «string-like» object that uses the underlying file (instead of reading the whole file in memory):
import mmap
with open('example.txt') as f:
s = mmap.mmap(f.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ)
if s.find('blabla') != -1:
print('true')
NOTE: in python 3, mmaps behave like bytearray objects rather than strings, so the subsequence you look for with find() has to be a bytes object rather than a string as well, eg. s.find(b'blabla'):
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import mmap
with open('example.txt', 'rb', 0) as file,
mmap.mmap(file.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ) as s:
if s.find(b'blabla') != -1:
print('true')
You could also use regular expressions on mmap e.g., case-insensitive search: if re.search(br'(?i)blabla', s):
In this Python tutorial, you’ll learn to search a string in a text file. Also, we’ll see how to search a string in a file and print its line and line number.
After reading this article, you’ll learn the following cases.
- If a file is small, read it into a string and use the
find()method to check if a string or word is present in a file. (easier and faster than reading and checking line per line) - If a file is large, use the mmap to search a string in a file. We don’t need to read the whole file in memory, which will make our solution memory efficient.
- Search a string in multiple files
- Search file for a list of strings
We will see each solution one by one.
Table of contents
- How to Search for a String in Text File
- Example to search for a string in text file
- Search file for a string and Print its line and line number
- Efficient way to search string in a large text file
- mmap to search for a string in text file
- Search string in multiple files
- Search file for a list of strings
How to Search for a String in Text File
Use the file read() method and string class find() method to search for a string in a text file. Here are the steps.
- Open file in a read mode
Open a file by setting a file path and access mode to the
open()function. The access mode specifies the operation you wanted to perform on the file, such as reading or writing. For example, r is for reading.fp= open(r'file_path', 'r') - Read content from a file
Once opened, read all content of a file using the
read()method. Theread()method returns the entire file content in string format. - Search for a string in a file
Use the
find()method of a str class to check the given string or word present in the result returned by theread()method. Thefind()method. The find() method will return -1 if the given text is not present in a file - Print line and line number
If you need line and line numbers, use the
readlines() method instead ofread()method. Use the for loop andreadlines()method to iterate each line from a file. Next, In each iteration of a loop, use the if condition to check if a string is present in a current line and print the current line and line number
Example to search for a string in text file
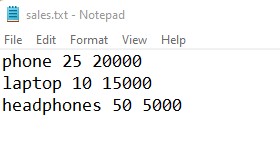
I have a ‘sales.txt’ file that contains monthly sales data of items. I want the sales data of a specific item. Let’s see how to search particular item data in a sales file.
def search_str(file_path, word):
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
# read all content of a file
content = file.read()
# check if string present in a file
if word in content:
print('string exist in a file')
else:
print('string does not exist in a file')
search_str(r'E:demosfiles_demosaccountsales.txt', 'laptop')Output:
string exists in a file
Search file for a string and Print its line and line number
Use the following steps if you are searching a particular text or a word in a file, and you want to print a line number and line in which it is present.
- Open a file in a read mode.
- Next, use the
readlines()method to get all lines from a file in the form of a list object. - Next, use a loop to iterate each line from a file.
- Next, In each iteration of a loop, use the if condition to check if a string is present in a current line and print the current line and line number.
Example: In this example, we’ll search the string ‘laptop’ in a file, print its line along with the line number.
# string to search in file
word = 'laptop'
with open(r'E:demosfiles_demosaccountsales.txt', 'r') as fp:
# read all lines in a list
lines = fp.readlines()
for line in lines:
# check if string present on a current line
if line.find(word) != -1:
print(word, 'string exists in file')
print('Line Number:', lines.index(line))
print('Line:', line)Output:
laptop string exists in a file line: laptop 10 15000 line number: 1
Note: You can also use the readline() method instead of readlines() to read a file line by line, stop when you’ve gotten to the lines you want. Using this technique, we don’t need to read the entire file.
Efficient way to search string in a large text file
All above way read the entire file in memory. If the file is large, reading the whole file in memory is not ideal.
In this section, we’ll see the fastest and most memory-efficient way to search a string in a large text file.
- Open a file in read mode
- Use for loop with
enumerate()function to get a line and its number. Theenumerate()function adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in enumerate object. Pass the file pointer returned by theopen()function to theenumerate(). - We can use this enumerate object with a for loop to access the each line and line number.
Note: The enumerate(file_pointer) doesn’t load the entire file in memory, so this is an efficient solution.
Example:
with open(r"E:demosfiles_demosaccountsales.txt", 'r') as fp:
for l_no, line in enumerate(fp):
# search string
if 'laptop' in line:
print('string found in a file')
print('Line Number:', l_no)
print('Line:', line)
# don't look for next lines
breakExample:
string found in a file Line Number: 1 Line: laptop 10 15000
mmap to search for a string in text file
In this section, we’ll see the fastest and most memory-efficient way to search a string in a large text file.
Also, you can use the mmap module to find a string in a huge file. The mmap.mmap() method creates a bytearray object that checks the underlying file instead of reading the whole file in memory.
Example:
import mmap
with open(r'E:demosfiles_demosaccountsales.txt', 'rb', 0) as file:
s = mmap.mmap(file.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ)
if s.find(b'laptop') != -1:
print('string exist in a file')Output:
string exist in a file
Search string in multiple files
Sometimes you want to search a string in multiple files present in a directory. Use the below steps to search a text in all files of a directory.
- List all files of a directory
- Read each file one by one
- Next, search for a word in the given file. If found, stop reading the files.
Example:
import os
dir_path = r'E:demosfiles_demosaccount'
# iterate each file in a directory
for file in os.listdir(dir_path):
cur_path = os.path.join(dir_path, file)
# check if it is a file
if os.path.isfile(cur_path):
with open(cur_path, 'r') as file:
# read all content of a file and search string
if 'laptop' in file.read():
print('string found')
breakOutput:
string found
Search file for a list of strings
Sometimes you want to search a file for multiple strings. The below example shows how to search a text file for any words in a list.
Example:
words = ['laptop', 'phone']
with open(r'E:demosfiles_demosaccountsales.txt', 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
# Iterate list to find each word
for word in words:
if word in content:
print('string exist in a file')Output:
string exist in a file
Python Exercises and Quizzes
Free coding exercises and quizzes cover Python basics, data structure, data analytics, and more.
- 15+ Topic-specific Exercises and Quizzes
- Each Exercise contains 10 questions
- Each Quiz contains 12-15 MCQ
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
In this article, we are going to see how to search for a string in text files using Python
Example:
string = “GEEK FOR GEEKS”
Input: “FOR”
Output: Yes, FOR is present in the given string.
Text File for demonstration:
myfile.txt
Finding the index of the string in the text file using readline()
In this method, we are using the readline() function, and checking with the find() function, this method returns -1 if the value is not found and if found it returns 0.
Python3
with open(r'myfile.txt', 'r') as fp:
lines = fp.readlines()
for row in lines:
word = 'Line 3'
if row.find(word) != -1:
print('string exists in file')
print('line Number:', lines.index(row))
Output:
string exists in file line Number: 2
Finding string in a text file using read()
we are going to search string line by line if the string is found then we will print that string and line number using the read() function.
Python3
with open(r'myfile.txt', 'r') as file:
content = file.read()
if 'Line 8' in content:
print('string exist')
else:
print('string does not exist')
Output:
string does not exist
Search for a String in Text Files using enumerate()
We are just finding string is present in the file or not using the enumerate() in Python.
Python3
with open(r"myfile.txt", 'r') as f:
for index, line in enumerate(f):
if 'Line 3y' in line:
print('string found in a file')
break
print('string does not exist in a file')
Output:
string does not exist in a file
Last Updated :
14 Mar, 2023
Like Article
Save Article
words = ['isotope', 'proton', 'electron', 'neutron']
def line_numbers(file_path, word_list):
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
results = {word:[] for word in word_list}
for num, line in enumerate(f, start=1):
for word in word_list:
if word in line:
results[word].append(num)
return results
This will return a dictionary that has all the occurrences of the given word (case-sensitive).
DEMO
>>> words = ['isotope', 'proton', 'electron', 'neutron']
>>> result = line_numbers(file_path, words)
>>> for word, lines in result.items():
print(word, ": ", ', '.join(lines))
# in your example, this would output:
isotope 1
proton 3
electron 2
neutron 5
Стоимость заказа
Имеется текстовый файл prices.txt с информацией о заказе из интернет магазина. В нем каждая строка с помощью символа табуляции t разделена на три колонки:
- наименование товара;
- количество товара (целое число);
- цена (в рублях) товара за 1 шт. (целое число).
Напишите программу, подсчитывающую общую стоимость заказа.
Решение
Способ 1:
from operator import mul
with open('prices.txt') as file:
print(sum(map(lambda line: mul(*map(int, line.split()[1:])), file)))
Способ 2:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('prices.txt', sep ='t', header = None)
df.columns = ['Товар', 'Количество', 'Цена']
df['Итого'] = df['Количество'] * df['Цена']
summa_zakaza = sum(df['Итого'])
print(summa_zakaza)
Способ 3:
with open('prices.txt') as f:
print(sum(eval('*'.join(s.split()[1:])) for s in f))
Способ 4:
with open('prices.txt') as f:
print(sum(map(lambda x: int(x[1]) * int(x[2]), map(str.split, f.readlines()))))
Способ 5:
from functools import reduce
with open('prices.txt') as f:
file = open('prices.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8')
print(reduce(lambda x, y: x + int(y[1]) * int(y[2]), [i.split('t') for i in [i.strip() for i in file.readlines()]], 0))
Поиск слова в текстовом файле
Напишите программу, которая принимает поисковый запрос и выводит названия текстовых файлов, содержащих искомую подстроку. Все файлы располагаются в директории D:PythonTextfiles.
Формат ввода
Строка, содержащая поисковый запрос.
Формат вывода
Список текстовых файлов, содержащих введенную пользователем подстроку.
Пример ввода:
словарь
Пример вывода:
challenges-for-beginners-5.md
dictionaries-2.md
dictionaries.md
challenges-for-beginners.md
merge-dictionaries.md
dictionaries-4.md
dictionaries-3.md
Решение
Поскольку слово может встречаться в одном и том же файле несколько раз, есть смысл сохранять результаты поиска во множестве set.
import os
if __name__ == '__main__':
folder = 'D:\Python\Textfiles'
answ = set()
search = input()
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
filepath = os.path.join(folder, filename)
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as fp:
for line in fp:
if search in line:
answ.add(filename)
for i in answ:
print(i)
Словарь из CSV-файла
Имеется файл data.csv, содержащий информацию в csv-формате. Напишите функцию read_csv() для чтения данных из этого файла. Она должна возвращать список словарей, интерпретируя первую строку как имена ключей, а каждую последующую строку как значения этих ключей. Функция read_csv() не должна принимать аргументов.
Решение
Способ 1:
import csv
def read_csv():
with open("data.csv") as f:
a = [{k: v for k, v in row.items()}
for row in csv.DictReader(f, skipinitialspace=True)]
return a
Способ 2:
def read_csv():
with open('data.csv') as file:
keys = file.readline().strip().split(',')
return [dict(zip(keys, line.strip().split(','))) for line in file]
Способ 3:
def read_csv():
with open('data.csv', encoding='utf-8') as file:
info = list(map(lambda x: x.strip().split(','), file.readlines()))
return [dict(zip(info[0], j)) for j in info[1:]]
Способ 4:
from csv import DictReader
def read_csv():
with open('data.csv') as file_object:
data = DictReader(file_object)
ans = list(data)
return ans
Способ 5:
def read_csv():
with open("data.csv") as data_file:
dict_list = []
keys = data_file.readline().strip().split(",")
for values in data_file:
dict_list.append(dict(zip(keys, values.strip().split(","))))
return dict_list
Информация о файле
Имеется файл file.txt с текстом на латинице. Напишите программу, которая выводит следующую статистику по тексту:
- количество букв латинского алфавита;
- число слов;
- число строк.
Пример ввода и вывода
Предположим, что file.txt содержит приведенный ниже текст:
Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
В этом случае программа должна вывести информацию о файле в следующем виде:
Input file contains:
108 letters
20 words
4 lines
Решение
Способ 1:
with open('file.txt') as f:
txt = f.read()
print('Input file contains:')
print(sum(map(str.isalpha, txt)), 'letters')
print(len(txt.split()), 'words')
print(txt.count('n') + 1, 'lines')
Способ 2:
with open('file.txt') as f:
res = f.readlines()
f.seek(0)
words = f.read().split()
let = sum(len([y for y in x if y.isalpha()]) for x in words)
print('Input file contains:')
print(f'{let} letters')
print(f'{len(words)} words')
print(f'{len(res)} lines')
Способ 3:
with open('file.txt') as f:
print('Input file contains:')
print(len(list(filter(lambda x: x.isalpha(), f.read()))), 'letters')
f.seek(0)
print(len(f.read().split()), 'words')
f.seek(0)
print(len(list(f.readlines())), 'lines')
Способ 4:
with open('file.txt') as file:
lst = file.read()
lines = lst.count('n') + 1
words = len(lst.split())
letters = len([c for c in lst if c.isalpha()])
print(f'Input file contains:n{letters} lettersn{words} wordsn{lines} lines')
Способ 5:
with open('file.txt') as f:
t = f.read()
f.seek(0)
print('Input file contains:')
print(f'{len(list(filter(str.isalpha, t)))} letters')
print(f'{len(t.split())} words')
print(f'{len(f.readlines())} lines')
Запрещенные слова
Напишите программу, которая получает на вход строку с названием текстового файла, и выводит на экран содержимое этого файла, заменяя все запрещенные слова звездочками * (количество звездочек равно количеству букв в слове). Запрещенные слова, разделенные символом пробела, хранятся в текстовом файле forbidden_words.txt. Все слова в этом файле записаны в нижнем регистре. Программа должна заменить запрещенные слова, где бы они ни встречались, даже в середине другого слова. Замена производится независимо от регистра: если файл forbidden_words.txt содержит запрещенное слово exam, то слова exam, Exam, ExaM, EXAM и exAm должны быть заменены на ****.
Формат ввода
Строка текста с именем существующего текстового файла, в котором необходимо заменить запрещенные слова звездочками.
Формат вывода
Текст, отредактированный в соответствии с условием задачи.
Пример ввода вывода
Предположим, что forbidden_words.txt содержит следующие запрещенные слова:
hello email python the exam wor is
А текст файла, подлежащего цензуре, выглядит так:
Hello, world! Python IS the programming language of thE future. My EMAIL is....
PYTHON is awesome!!!!
Тогда программа должна вывести отредактированный текст в таком виде:
*****, ***ld! ****** ** *** programming language of *** future. My ***** **....
****** ** awesome!!!!
Решение
Способ 1:
with open('forbidden_words.txt') as forbidden_words, open(input()) as to_change:
pattern, text = forbidden_words.read().split(), to_change.read()
text_lower = text.lower()
for word in pattern:
text_lower = text_lower.replace(word, '*' * len(word))
result = ''.join((y, x)[x == '*'] for x, y in zip(text_lower, text))
print(result)
Способ 2:
with open('forbidden_words.txt') as f:
forbidden_words = {word: '*' * len(word) for word in f.read().split()}
with open(input()) as f:
s = f.read()
s_lower = s.lower()
for forbidden_word in forbidden_words:
s_lower = s_lower.replace(forbidden_word, forbidden_words[forbidden_word])
print(*map((lambda c1, c2: '*' if c2 == '*' else c1), s, s_lower), sep='')
Способ 3:
with open("forbidden_words.txt", encoding="utf-8") as file, open(input()) as infile:
text = infile.read()
for f in file.read().strip("n").split():
pos = text.lower().find(f)
while pos > -1:
text = text[:pos] + "*" * len(f) + text[pos+len(f):]
pos = text.lower().find(f)
print(text)
Способ 4:
import re
with open(input()) as inp, open('forbidden_words.txt') as fw:
text, forbidden = inp.read(), fw.read().split()
for i in forbidden:
text = re.sub(i, '*' * len(i), text, flags=re.I)
print(text)
Способ 5:
with open(input(), encoding='utf-8') as r, open('forbidden_words.txt', encoding='utf-8') as s:
w = s.read().split()
v = r.read()
l = v.lower()
for i in w:
l = l.replace(i, '*' * len(i))
[print(j if j == '*' else i, end='') for i, j in zip(v, l)]
***
Материалы по теме
- 🐍 Задача о поврежденной XML-строке
- 🐍 5 задач с решениями на Python для начинающих разработчиков
- 🐍 5 классических задач по Python для начинающих с решениями