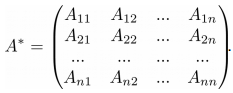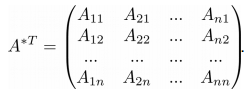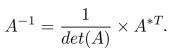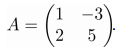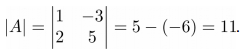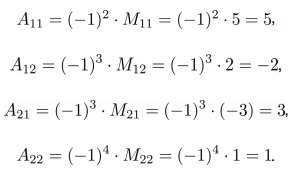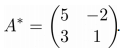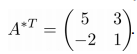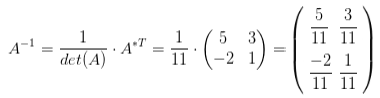1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 |
#include <iostream> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> using namespace std; template <typename T> void FreeMem(T **matr, int n); template <typename T> void PrintMtx(T **matr, int n); template <typename T> void SetMtx(T **matr, int n); template <typename T> void TransponMtx(T **matr, T **tMatr, int n); void Get_matr(int **matr, int n, int **temp_matr, int indRow, int indCol); int Det(int **matr, int n); void main() { srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); setlocale(0, ""); int n, det; cout << "Введите размер матрицы: "; cin >> n; int **matr = new int * [n]; double **obr_matr = new double * [n]; double **tobr_matr = new double * [n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ matr[i] = new int[n]; obr_matr[i] = new double[n]; tobr_matr[i] = new double[n]; } SetMtx(matr, n); PrintMtx(matr, n); det = Det(matr, n); cout << "Определитель матрицы = " << det << endl; if(det){ for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ int m = n - 1; int **temp_matr = new int * [m]; for(int k = 0; k < m; k++) temp_matr[k] = new int[m]; Get_matr(matr, n, temp_matr, i, j); obr_matr[i][j] = pow(-1.0, i + j + 2) * Det(temp_matr, m) / det; FreeMem(temp_matr, m); } } } else cout << "Т.к. определитель матрицы = 0,nто матрица вырожденная и обратной не имеет!!!" << endl; //Транспонирование матрицы TransponMtx(obr_matr, tobr_matr, n); //Печать обратной матрицы после транспонирования PrintMtx(tobr_matr, n); FreeMem(tobr_matr, n); FreeMem(matr, n); FreeMem(obr_matr, n); } //Функция транспонирования матрицы template <typename T> void TransponMtx(T **matr, T **tMatr, int n){// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) tMatr[j][i] = matr[i][j]; } //Функция освобождения памяти template <typename T> void FreeMem(T **matr, int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) delete [] matr[i]; delete [] matr; } //функция заполнения матрицы template <typename T> void SetMtx(T **matr, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) matr[i][j] = rand()%9 + 1; } //функция печати матрицы template <typename T> void PrintMtx(T **matr, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) cout << matr[i][j] << " "; cout << endl; } } //функция вычеркивания строки и столбца void Get_matr(int **matr, int n, int **temp_matr, int indRow, int indCol) { int ki = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(i != indRow){ for (int j = 0, kj = 0; j < n; j++){ if (j != indCol){ temp_matr[ki][kj] = matr[i][j]; kj++; } } ki++; } } } //============================================================================================================== // вычисление определителя //============================================================================================================== //функция вычисления определителя матрицы int Det(int **matr, int n) { int temp = 0; //временная переменная для хранения определителя int k = 1; //степень if(n < 1){ cout<<"Не верный размер матрицы!!!" << endl; return 0; } else if (n == 1) temp = matr[0][0]; else if (n == 2) temp = matr[0][0] * matr[1][1] - matr[1][0] * matr[0][1]; else{ for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ int m = n - 1; int **temp_matr = new int * [m]; for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) temp_matr[j] = new int [m]; Get_matr(matr, n, temp_matr, 0, i); temp = temp + k * matr[0][i] * Det(temp_matr, m); k = -k; FreeMem(temp_matr, m); } } return temp; } |
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Inverse function in MATLAB is used to find the inverse of a matrix. Suppose A is a matrix and B is the inverse of a then A*B will be an identity matrix. This function computes the inverse of a square matrix. This is used while solving linear equations. We can compute the inverse of a matrix by passing it to inv().
Syntax:
inv(A)
Parameters:
It takes a matrix as parameter.
Returns:
It returns a matrix which is inverse of input matrix.
Below are some examples which depict how to compute the inverse of a matrix in MATLAB.
Example 1: This example takes a 3×3 matrix as input and computes its inverse using inv() function.
Matlab
A = [1 2 0; 3 1 4; 5 6 7]
inv(A)
Output:
Example 2: Here is another example that takes a 2×2 matrix as input and computes its inverse.
Matlab
Output:
Example 3: This example uses a singular matrix and tries to find its inverse. It will show a warning that the matrix is a singular matrix. Different versions of MATLAB gave a different value of inverse for singular matrix. This is due to the different versions of Math Kernel Library used in different versions of MATLAB.
Matlab
A = [2 4 6;2 0 2;6 8 14]
inv(A)
Output:
warning: matrix singular to machine precision, rcond = 1.34572e-17
Last Updated :
28 Apr, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int matrix[20][20], r,a;
int i, j, k, m;
scanf_s("%d", &m);
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
scanf_s("%i", &matrix[i][j]);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = m; j < 2*m; j++)
{
if(i == (j - m))
matrix[i][j] = 1;
else
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if(i != j)
{
r = matrix[j][i]/matrix[i][i];
for(k = 0; k < 2*m; k++)
{
matrix[j][k] -= r * matrix[i][k];
}
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
a = matrix[i][i];
for(j = 0; j < 2*m; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] /= a;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = m; j < 2*m; j++)
{
printf("%it", matrix[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
return 0;
}
//Title: Matrix Header File
//Writer: Say OL
//This is a beginner code not an expert one
//No responsibilty for any errors
//Use for your own risk
using namespace std;
int row,col,Row,Col;
double Coefficient;
//Input Matrix
void Input(double Matrix[9][9],int Row,int Col)
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
{
cout<<"e["<<row<<"]["<<col<<"]=";
cin>>Matrix[row][col];
}
}
//Output Matrix
void Output(double Matrix[9][9],int Row,int Col)
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
{
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
cout<<Matrix[row][col]<<"t";
cout<<endl;
}
}
//Copy Pointer to Matrix
void CopyPointer(double (*Pointer)[9],double Matrix[9][9],int Row,int Col)
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
Matrix[row][col]=Pointer[row][col];
}
//Copy Matrix to Matrix
void CopyMatrix(double MatrixInput[9][9],double MatrixTarget[9][9],int Row,int Col)
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixTarget[row][col]=MatrixInput[row][col];
}
//Transpose of Matrix
double MatrixTran[9][9];
double (*(Transpose)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Row,int Col))[9]
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixTran[col][row]=MatrixInput[row][col];
return MatrixTran;
}
//Matrix Addition
double MatrixAdd[9][9];
double (*(Addition)(double MatrixA[9][9],double MatrixB[9][9],int Row,int Col))[9]
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixAdd[row][col]=MatrixA[row][col]+MatrixB[row][col];
return MatrixAdd;
}
//Matrix Subtraction
double MatrixSub[9][9];
double (*(Subtraction)(double MatrixA[9][9],double MatrixB[9][9],int Row,int Col))[9]
{
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixSub[row][col]=MatrixA[row][col]-MatrixB[row][col];
return MatrixSub;
}
//Matrix Multiplication
int mRow,nCol,pCol,kcol;
double MatrixMult[9][9];
double (*(Multiplication)(double MatrixA[9][9],double MatrixB[9][9],int mRow,int nCol,int pCol))[9]
{
for(row=1;row<=mRow;row++)
for(col=1;col<=pCol;col++)
{
MatrixMult[row][col]=0.0;
for(kcol=1;kcol<=nCol;kcol++)
MatrixMult[row][col]+=MatrixA[row][kcol]*MatrixB[kcol][col];
}
return MatrixMult;
}
//Interchange Two Rows
double RowTemp[9][9];
double MatrixInter[9][9];
double (*(InterchangeRow)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Row,int Col,int iRow,int jRow))[9]
{
CopyMatrix(MatrixInput,MatrixInter,Row,Col);
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
{
RowTemp[iRow][col]=MatrixInter[iRow][col];
MatrixInter[iRow][col]=MatrixInter[jRow][col];
MatrixInter[jRow][col]=RowTemp[iRow][col];
}
return MatrixInter;
}
//Pivote Downward
double MatrixDown[9][9];
double (*(PivoteDown)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Row,int Col,int tRow,int tCol))[9]
{
CopyMatrix(MatrixInput,MatrixDown,Row,Col);
Coefficient=MatrixDown[tRow][tCol];
if(Coefficient!=1.0)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixDown[tRow][col]/=Coefficient;
if(tRow<Row)
for(row=tRow+1;row<=Row;row++)
{
Coefficient=MatrixDown[row][tCol];
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixDown[row][col]-=Coefficient*MatrixDown[tRow][col];
}
return MatrixDown;
}
//Pivote Upward
double MatrixUp[9][9];
double (*(PivoteUp)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Row,int Col,int tRow,int tCol))[9]
{
CopyMatrix(MatrixInput,MatrixUp,Row,Col);
Coefficient=MatrixUp[tRow][tCol];
if(Coefficient!=1.0)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixUp[tRow][col]/=Coefficient;
if(tRow>1)
for(row=tRow-1;row>=1;row--)
{
Coefficient=MatrixUp[row][tCol];
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
MatrixUp[row][col]-=Coefficient*MatrixUp[tRow][col];
}
return MatrixUp;
}
//Pivote in Determinant
double MatrixPiv[9][9];
double (*(Pivote)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Dim,int pTarget))[9]
{
CopyMatrix(MatrixInput,MatrixPiv,Dim,Dim);
for(row=pTarget+1;row<=Dim;row++)
{
Coefficient=MatrixPiv[row][pTarget]/MatrixPiv[pTarget][pTarget];
for(col=1;col<=Dim;col++)
{
MatrixPiv[row][col]-=Coefficient*MatrixPiv[pTarget][col];
}
}
return MatrixPiv;
}
//Determinant of Square Matrix
int dCounter,dRow;
double Det;
double MatrixDet[9][9];
double Determinant(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Dim)
{
CopyMatrix(MatrixInput,MatrixDet,Dim,Dim);
Det=1.0;
if(Dim>1)
{
for(dRow=1;dRow<Dim;dRow++)
{
dCounter=dRow;
while((MatrixDet[dRow][dRow]==0.0)&(dCounter<=Dim))
{
dCounter++;
Det*=-1.0;
CopyPointer(InterchangeRow(MatrixDet,Dim,Dim,dRow,dCounter),MatrixDet,Dim,Dim);
}
if(MatrixDet[dRow][dRow]==0)
{
Det=0.0;
break;
}
else
{
Det*=MatrixDet[dRow][dRow];
CopyPointer(Pivote(MatrixDet,Dim,dRow),MatrixDet,Dim,Dim);
}
}
Det*=MatrixDet[Dim][Dim];
}
else Det=MatrixDet[1][1];
return Det;
}
//Matrix Identity
double MatrixIdent[9][9];
double (*(Identity)(int Dim))[9]
{
for(row=1;row<=Dim;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Dim;col++)
if(row==col)
MatrixIdent[row][col]=1.0;
else
MatrixIdent[row][col]=0.0;
return MatrixIdent;
}
//Join Matrix to be Augmented Matrix
double MatrixJoin[9][9];
double (*(JoinMatrix)(double MatrixA[9][9],double MatrixB[9][9],int Row,int ColA,int ColB))[9]
{
Col=ColA+ColB;
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Col;col++)
if(col<=ColA)
MatrixJoin[row][col]=MatrixA[row][col];
else
MatrixJoin[row][col]=MatrixB[row][col-ColA];
return MatrixJoin;
}
//Inverse of Matrix
double (*Pointer)[9];
double IdentMatrix[9][9];
int Counter;
double MatrixAug[9][9];
double MatrixInv[9][9];
double (*(Inverse)(double MatrixInput[9][9],int Dim))[9]
{
Row=Dim;
Col=Dim+Dim;
Pointer=Identity(Dim);
CopyPointer(Pointer,IdentMatrix,Dim,Dim);
Pointer=JoinMatrix(MatrixInput,IdentMatrix,Dim,Dim,Dim);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixAug,Row,Col);
for(Counter=1;Counter<=Dim;Counter++)
{
Pointer=PivoteDown(MatrixAug,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixAug,Row,Col);
}
for(Counter=Dim;Counter>1;Counter--)
{
Pointer=PivoteUp(MatrixAug,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixAug,Row,Col);
}
for(row=1;row<=Dim;row++)
for(col=1;col<=Dim;col++)
MatrixInv[row][col]=MatrixAug[row][col+Dim];
return MatrixInv;
}
//Gauss-Jordan Elemination
double MatrixGJ[9][9];
double VectorGJ[9][9];
double (*(GaussJordan)(double MatrixInput[9][9],double VectorInput[9][9],int Dim))[9]
{
Row=Dim;
Col=Dim+1;
Pointer=JoinMatrix(MatrixInput,VectorInput,Dim,Dim,1);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGJ,Row,Col);
for(Counter=1;Counter<=Dim;Counter++)
{
Pointer=PivoteDown(MatrixGJ,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGJ,Row,Col);
}
for(Counter=Dim;Counter>1;Counter--)
{
Pointer=PivoteUp(MatrixGJ,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGJ,Row,Col);
}
for(row=1;row<=Dim;row++)
for(col=1;col<=1;col++)
VectorGJ[row][col]=MatrixGJ[row][col+Dim];
return VectorGJ;
}
//Generalized Gauss-Jordan Elemination
double MatrixGGJ[9][9];
double VectorGGJ[9][9];
double (*(GeneralizedGaussJordan)(double MatrixInput[9][9],double VectorInput[9][9],int Dim,int vCol))[9]
{
Row=Dim;
Col=Dim+vCol;
Pointer=JoinMatrix(MatrixInput,VectorInput,Dim,Dim,vCol);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGGJ,Row,Col);
for(Counter=1;Counter<=Dim;Counter++)
{
Pointer=PivoteDown(MatrixGGJ,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGGJ,Row,Col);
}
for(Counter=Dim;Counter>1;Counter--)
{
Pointer=PivoteUp(MatrixGGJ,Row,Col,Counter,Counter);
CopyPointer(Pointer,MatrixGGJ,Row,Col);
}
for(row=1;row<=Row;row++)
for(col=1;col<=vCol;col++)
VectorGGJ[row][col]=MatrixGGJ[row][col+Dim];
return VectorGGJ;
}
//Matrix Sparse, Three Diagonal Non-Zero Elements
double MatrixSpa[9][9];
double (*(Sparse)(int Dimension,double FirstElement,double SecondElement,double ThirdElement))[9]
{
MatrixSpa[1][1]=SecondElement;
MatrixSpa[1][2]=ThirdElement;
MatrixSpa[Dimension][Dimension-1]=FirstElement;
MatrixSpa[Dimension][Dimension]=SecondElement;
for(int Counter=2;Counter<Dimension;Counter++)
{
MatrixSpa[Counter][Counter-1]=FirstElement;
MatrixSpa[Counter][Counter]=SecondElement;
MatrixSpa[Counter][Counter+1]=ThirdElement;
}
return MatrixSpa;
}
Copy and save the above code as Matrix.h then try the following code:
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include"Matrix.h"
int Dim;
double Matrix[9][9];
int main()
{
cout<<"Enter your matrix dimension: ";
cin>>Dim;
Input(Matrix,Dim,Dim);
cout<<"Your matrix:"<<endl;
Output(Matrix,Dim,Dim);
cout<<"The inverse:"<<endl;
Output(Inverse(Matrix,Dim),Dim,Dim);
getch();
}
Пятый урок посвящен нахождению обратной матрицы, ее свойствам, а также определению ранга матрицы
- Обратная матрица
- Ранг матрицы
Обратная матрица
Обратной матрицей A-1 матрицы A называют матрицу, удовлетворяющую следующему равенству:
где – E это единичная матрица.
Для того, чтобы у квадратной матрицы A была обратная матрица необходимо и достаточно чтобы определитель |A| был не равен нулю. Введем понятие союзной матрицы. Союзная матрица A* строится на базе исходной A путем замены всех элементов матрицы A на их алгебраические дополнения.
Исходная матрица:
Союзная ей матрица A*:
Транспонируя матрицу A*, мы получим так называемую присоединенную матрицу A*T:
Теперь, зная как вычислять определитель и присоединенную матрицу, мы можем определить матрицу A-1, обратную матрице A:
➣ Численный пример
Пример вычисления обратной матрицы. Пусть дана исходная матрица A, следующего вида:
Для начала найдем определитель матрицы A:
Как видно из приведенных вычислений, определитель матрицы не равен нулю, значит у матрицы A есть обратная. Построим присоединенную матрицу, для этого вычислим алгебраические дополнения для каждого элемента матрицы A:
Союзная матрица будет иметь следующий вид:
Присоединенная матрица получается из союзной путем транспонирования:
Находим обратную матрицу:
➤ Пример на Python
Решим задачу определения обратной матрицы на Python. Для получения обратной матрицы будем использовать функцию inv():
>>> A = np.matrix('1 -3; 2 5')
>>> A_inv = np.linalg.inv(A)
>>> print(A_inv)
[[ 0.45454545 0.27272727]
[-0.18181818 0.09090909]]
Рассмотрим свойства обратной матрицы.
Свойство 1. Обратная матрица обратной матрицы есть исходная матрица:
➤Пример на Python
>>> A = np.matrix('1. -3.; 2. 5.')
>>> A_inv = np.linalg.inv(A)
>>> A_inv_inv = np.linalg.inv(A_inv)
>>> print(A)
[[1. -3.]
[2. 5.]]
>>> print(A_inv_inv)
[[1. -3.]
[2. 5.]]
Свойство 2. Обратная матрица транспонированной матрицы равна транспонированной матрице от обратной матрицы:
➤ Пример на Python
>>> A = np.matrix('1. -3.; 2. 5.')
>>> L = np.linalg.inv(A.T)
>>> R = (np.linalg.inv(A)).T
>>> print(L)
[[ 0.45454545 -0.18181818]
[ 0.27272727 0.09090909]]
>>> print(R)
[[ 0.45454545 -0.18181818]
[ 0.27272727 0.09090909]]
Свойство 3. Обратная матрица произведения матриц равна произведению обратных матриц:
➤ Пример на Python
>>> A = np.matrix('1. -3.; 2. 5.')
>>> B = np.matrix('7. 6.; 1. 8.')
>>> L = np.linalg.inv(A.dot(B))
>>> R = np.linalg.inv(B).dot(np.linalg.inv(A))
>>> print(L)
[[ 0.09454545 0.03272727]
[-0.03454545 0.00727273]]
>>> print(R)
[[ 0.09454545 0.03272727]
[-0.03454545 0.00727273]]
Ранг матрицы
Ранг матрицы является еще одной важной численной характеристикой. Рангом называют максимальное число линейно независимых строк (столбцов) матрицы. Линейная независимость означает, что строки (столбцы) не могут быть линейно выражены через другие строки (столбцы). Ранг матрицы можно найти через ее миноры, он равен наибольшему порядку минора, который не равен нулю. Существование ранга у матрицы не зависит от того квадратная она или нет.
Вычислим ранг матрицы с помощью Python. Создадим единичную матрицу:
>>> m_eye = np.eye(4) >>> print(m_eye) [[1. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 1. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 1.]]
Ранг такой матрицы равен количеству ее столбцов (или строк), в нашем случае ранг будет равен четырем, для его вычисления на Python воспользуемся функцией matrix_rank():
>>> rank = np.linalg.matrix_rank(m_eye) >>> print(rank) 4
Если мы приравняем элемент в нижнем правом углу к нулю, то ранг станет равен трем:
>>> m_eye[3][3] = 0 >>> print(m_eye) [[1. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 1. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.]] >>> rank = np.linalg.matrix_rank(m_eye) >>> print(rank) 3
P.S.
Вводные уроки по “Линейной алгебре на Python” вы можете найти соответствующей странице нашего сайта. Все уроки по этой теме собраны в книге “Линейная алгебра на Python”.
Если вам интересна тема анализа данных, то мы рекомендуем ознакомиться с библиотекой Pandas. Для начала вы можете познакомиться с вводными уроками. Все уроки по библиотеке Pandas собраны в книге “Pandas. Работа с данными”.